Orchestrating Test Runs Across Application Layers with TurboRepo
In this post, we'll explore the advantages of using TurboRepo to orchestrate test runs across different layers of your application. Specifically, we'll focus on unit tests executed within a GitHub CI pipeline. By leveraging TurboRepo, we can validate all domain use cases before pushing changes, ensuring that business rules remain intact without coupling to infrastructure or user interface concerns. This approach aligns with SOLID principles, particularly SRP (Single Responsibility Principle), OCP (Open-Closed Principle), and DIP (Dependency Inversion Principle).
Background
When working with complex applications, maintaining a robust test suite becomes crucial. Unit tests play a pivotal role in ensuring the correctness of individual components. However, managing test execution across various layers—such as domain, application, and infrastructure—can be challenging.
TurboRepo: A Solution for Test Orchestration
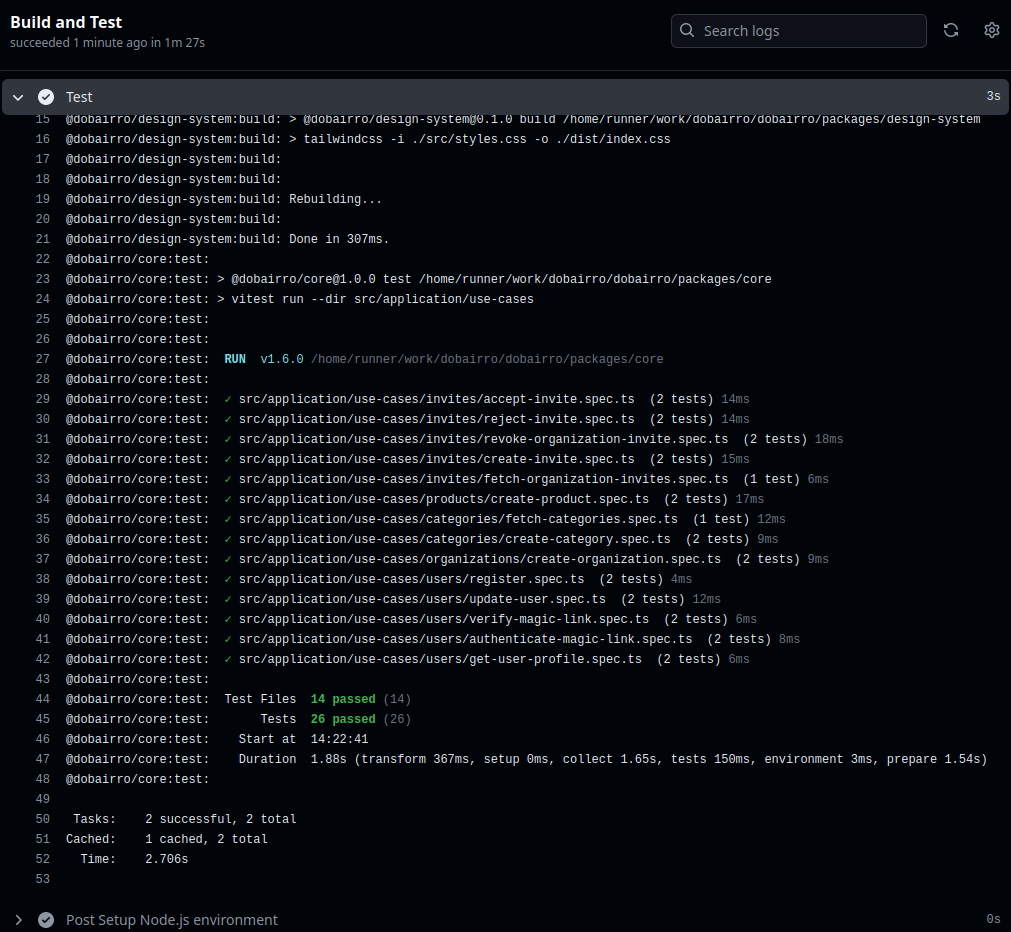
TurboRepo simplifies test orchestration by providing a unified interface for triggering tests across different layers. Let's dive into how it works:
-
Layer-Specific Test Suites:
- Define separate test suites for each layer (e.g., domain, application, infrastructure).
- These test suites should cover all relevant use cases and business logic.
-
CI Pipeline Integration:
- Set up a CI pipeline (e.g., GitHub Actions) to automatically trigger tests.
- Configure TurboRepo to execute the appropriate test suite based on the changes made.
-
Domain-Level Validation:
- Before pushing changes, TurboRepo runs the domain-specific test suite.
- This ensures that business rules are intact and that no unintended side effects occur.
-
Decoupling and SOLID Principles:
- By adhering to SOLID principles, we keep our codebase modular and maintainable.
- SRP ensures that each component has a single responsibility.
- OCP allows us to extend functionality without modifying existing code.
- DIP promotes loose coupling and dependency inversion.
Implementing an API Layer
Once we've completed domain and application code, implementing an API layer becomes straightforward. We'll use Fastify, a lightweight Node.js framework, to handle HTTP requests. Here's how it fits into our architecture:
-
API Layer Responsibilities:
- The API layer's sole responsibility is to handle HTTP requests.
- It communicates with the application layer (where business logic resides) via dependency injection.
-
Flexibility for the Future:
- If we decide to switch to a different technology stack, we can do so seamlessly.
- Creating a new infrastructure layer involves implementing services and repositories, following the same dependency inversion pattern.
Contribute to the Project
If you found this post helpful or have suggestions for improvement, feel free to check out the project repository on GitHub. You are welcome to fork the repository and submit a pull request. If you have any questions or want to discuss a topic, please open an issue. We appreciate your contributions!