Integrating unit and end-to-end tests with turborepo
Context
Comprehensive and reliable testing is essential when developing an application. This article explores integrating unit and end-to-end (E2E) tests using TurboRepo while ensuring a secure and isolated database for testing purposes.
Unit Testing
Unit tests focus on verifying small units or functions of code in isolation. They ensure that each component functions as expected, preventing bugs and providing confidence for future code changes. In our case, these tests specifically target the application layer, where all business rules reside.
End-to-End (E2E) Testing
End-to-end tests evaluate the entire system, simulating real user behavior from the front end to the database. They validate the entire application flow and identify integration issues. Common use cases include login flows, e-commerce transactions, and form submissions.
Isolating the Database
To ensure security and isolation during testing, create a dedicated database exclusively for running tests. This prevents interference with production data and maintains test integrity.
Code Examples
Singleton Pattern for Prisma Service
Here's how we can use the singleton pattern to create a PrismaService class that provides a single instance of the Prisma client:
// database/prisma.ts import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client' export class PrismaService extends PrismaClient { private static instance: PrismaClient public static getInstance(): PrismaClient { if (!PrismaService.instance) { PrismaService.instance = new PrismaClient({ log: ['warn', 'error'], }) } return PrismaService.instance } }
Repository Class for Category
Here’s how to use the PrismaService class to create a PrismaCategoryRepo class that interacts with the category table in the database:
// database/repositories/prisma-category-repo.ts import type { Category, CategoryRepo } from '@dobairro/core' import { PrismaCategoryMapper } from '@/database/mappers/prisma-category-mapper' import type { PrismaService } from '../prisma' export class PrismaCategoryRepo implements CategoryRepo { constructor(private db: PrismaService) {} public async create(category: Category): Promise<Category> { const data = PrismaCategoryMapper.toPrisma(category) const dbCategory = await this.db.category.create({ data, }) return PrismaCategoryMapper.toDomain(dbCategory) } public async delete(category: Category): Promise<void> { await this.db.category.delete({ where: { id: category.id.toString(), organizationId: category.organizationId.toString(), }, }) } public async findBySlug(slug: string): Promise<Category | null> { const category = await this.db.category.findUnique({ where: { slug, }, }) if (!category) { return null } return PrismaCategoryMapper.toDomain(category) } public async findById(categoryId: string): Promise<Category | null> { const category = await this.db.category.findUnique({ where: { id: categoryId, }, }) if (!category) { return null } return PrismaCategoryMapper.toDomain(category) } public async findManyByOrg(organizationId: string): Promise<Category[]> { const categories = await this.db.category.findMany({ where: { organizationId, }, }) return categories.map(PrismaCategoryMapper.toDomain) } }
Use Case Factory
In the controller, we use the makeCreateCategory function to create a new CreateCategoryUseCase instance that interacts with the PrismaCategoryRepo and PrismaOrganizationRepo classes:
// application/factories/make-create-category.ts import { CreateCategoryUseCase } from '@dobairro/core' import { PrismaService } from '@/database/prisma' import { PrismaCategoryRepo } from '@/database/repositories/prisma-category-repo' import { PrismaOrganizationRepo } from '@/database/repositories/prisma-organization-repo' export const makeCreateCategory = () => { const organizationRepo = new PrismaOrganizationRepo( PrismaService.getInstance(), ) const categoryRepo = new PrismaCategoryRepo(PrismaService.getInstance()) return new CreateCategoryUseCase(categoryRepo, organizationRepo) }
Controller Setup
Finally, we use the createCategoryController function to register the createCategory route in our Fastify application:
// controllers/create-category.ts import { NotAllowedError } from '@dobairro/core/src/application/use-cases/_errors/not-allowed-error' import type { FastifyInstance } from 'fastify' import type { ZodTypeProvider } from 'fastify-type-provider-zod' import { z } from 'zod' import { makeCreateCategory } from '@/application/factories/make-create-category' import { BadRequestError } from './_errors/bad-request-error' import { UnauthorizedError } from './_errors/unauthorized-error' import { auth } from './middleware/auth' export const createCategoryController = async (app: FastifyInstance) => { app .withTypeProvider<ZodTypeProvider>() .register(auth) .post( '/organizations/:organizationId/categories', { schema: { tags: ['Category'], summary: 'Create a new Category', params: z.object({ organizationId: z.string().uuid(), }), body: z.object({ title: z.string().min(3), }), response: { 201: z.object({ categoryId: z.string().uuid(), }), 400: z.object({ message: z.unknown(), }), 401: z.object({ message: z.string(), }), }, }, }, async (request, reply) => { const { userId } = await request.getCurrentUser() const { title } = request.body const { organizationId } = request.params const createCategory = makeCreateCategory() const result = await createCategory.execute({ authenticatedUserId: userId, organizationId, title, }) if (result.isLeft()) { const error = result.value switch (error.constructor) { case NotAllowedError: throw new UnauthorizedError(error.message) default: throw new BadRequestError(error.message) } } const category = result.value.category return reply.status(201).send({ categoryId: category.id.toString(), }) }, ) }
Vitest Configuration
For each workspace in the monorepo, create a vitest.config.ts file to configure the test environment and set up the necessary dependencies. Here’s how we set it up for end-to-end testing:
// vitest.config.ts import swc from 'unplugin-swc' import tsConfigPaths from 'vite-tsconfig-paths' import { defineConfig } from 'vitest/config' export default defineConfig({ test: { include: ['**/*.spec.ts'], globals: true, root: './', setupFiles: ['dotenv/config', './src/tests/setup-e2e.ts'], dir: 'src', }, plugins: [ tsConfigPaths(), swc.vite({ module: { type: 'es6' }, }), ], })
E2E Test Setup
Here is the setup-e2e.ts file that sets up the isolated database for each test run:
// src/tests/setup-e2e.ts import { execSync } from 'node:child_process' import { randomUUID } from 'node:crypto' import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client' import { config } from 'dotenv' import { env } from '@/env' config({ path: '.env', override: true, }) const db = new PrismaClient() const generateUniqueDbURL = (schemaId: string) => { if (!env.DB_URL) { throw new Error('DB_URL is not set') } const url = new URL(env.DB_URL) url.searchParams.set('schema', schemaId) return url.toString() } const schemaId = randomUUID() beforeAll(async () => { const e2eDbURL = generateUniqueDbURL(schemaId) process.env.DB_URL = e2eDbURL execSync('pnpm run db:deploy') await db.$connect() }) afterAll(async () => { await db.$executeRawUnsafe(`DROP SCHEMA IF EXISTS "${schemaId}" CASCADE`) await db.$disconnect() })
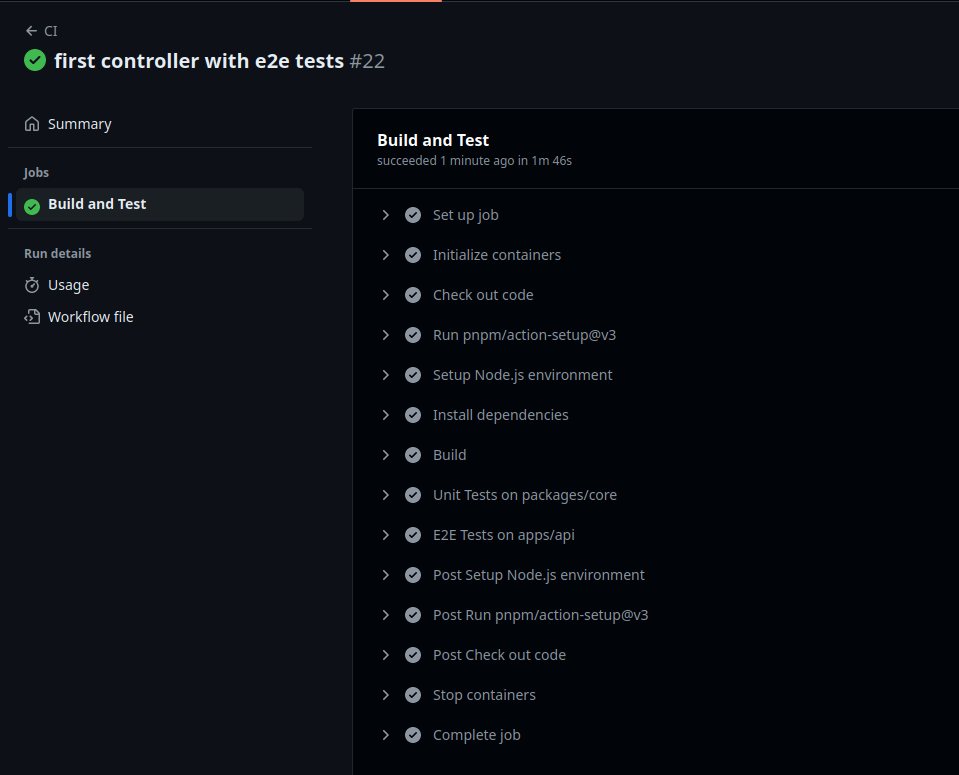
GitHub Workflow Setup
Finally, set up the GitHub workflow:
name: CI on: push: branches: ["main"] pull_request: types: [opened, synchronize] jobs: build: name: Build and Test timeout-minutes: 15 runs-on: ubuntu-latest services: postgres: image: bitnami/postgresql ports: - 5432:5432 env: POSTGRESQL_USERNAME: docker POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD: docker POSTGRESQL_DATABASE: dobairro env: JWT_SECRET: testing API_URL: http://localhost:4000 DB_URL: postgresql://docker:docker@localhost:5432/dobairro?schema=public steps: - name: Check out code uses: actions/checkout@v4 with: fetch-depth: 2 - uses: pnpm/action-setup@v3 with: version: 8 - name: Setup Node.js environment uses: actions/setup-node@v4 with: node-version: 20 cache: 'pnpm' - name: Install dependencies run: pnpm install - name: Build run: pnpm build - name: Unit Tests on packages/core run: | cd packages/core pnpm run test - name: E2E Tests on apps/api run: | cd apps/api pnpm run db:generate pnpm run db:deploy pnpm run test env: JWT_SECRET: testing API_URL: http://localhost:4000 DB_URL: postgresql://docker:docker@localhost:5432/dobairro?schema=public
Contribute to the Project
If you found this post helpful or have suggestions for improvement, feel free to check out the project repository on GitHub. You are welcome to fork the repository and submit a pull request. If you have any questions or want to discuss a topic, please open an issue. We appreciate your contributions!